 Bitmex
Bitmex9.1
This exchange was founded in 2014 but started gaining popularity in early 2018 when the ability to earn on a price decline was more relevant than ever. At the moment this is the leading exchange for margin trading, not only because of the largest number of members but also due to the highest level of liquidity.
Despite this, however, it is the biggest crypto margin exchange, very often its behaviour doesn’t correspond to its title: regular overloads and horrible lags became normal for this exchange users.
- High level of liquidity
- Secure Storage
- Good coin variety
- Regular overloads and lags
- No liquidity at sharp movements
- Not available for USA users
- Perpetual swap contract (XBT) instead of BTC
- Security 9.5/10
- Liquidity 8.5/10
- Fees 9/10
- Coin Variety 9/10
- UI/UX 9.5/10
Available Currencies & Fees
BitMEX allows us to trade 8 different crypto-currencies. Here is the list of them: Bitcoin, Ethereum, Litecoin, Ripple, Cardano, Bitcoin Cash, EOS, Tron.
Talking about fees, there are two types of commissions: “maker” and “taker”. “Maker” is used when a trader makes an order, and “taker” when it is executing.
When you use perpetual swaps, every 8 hours between traders funding processed — someone pays money to you or you have to pay. If you play “short”, while most of the traders hold “long” — then they pay you. If you are in the “long” as the majority, then you pay.
| Tron (TRX) | Leverage | Maker Fee | Taker Fees | Settlement Fee |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bitcoin (XBT) | 100x | -0.0250% | 0.0750% | 0.0500% |
| Bitcoin Cash (BCH) | 20x | -0.0500% | 0.0250% | 0.0000% |
| Cardano (ADA) | 20x | -0.0500% | 0.0250% | 0.0000% |
| EOS Token (EOS) | 20x | -0.0500% | 0.0250% | 0.0000% |
| Ethereum (ETH) | 20x | -0.0500% | 0.0250% | 0.0000% |
| Litecoin (LTC) | 33.3x | -0.0500% | 0.0250% | 0.0000% |
| Tron (TRX) | 20x | -0.0500% | 0.0250% | 0.0000% |
| Ripple (XRP) | 20x | -0.0500% | 0.0250% | 0.0000% |
Interface
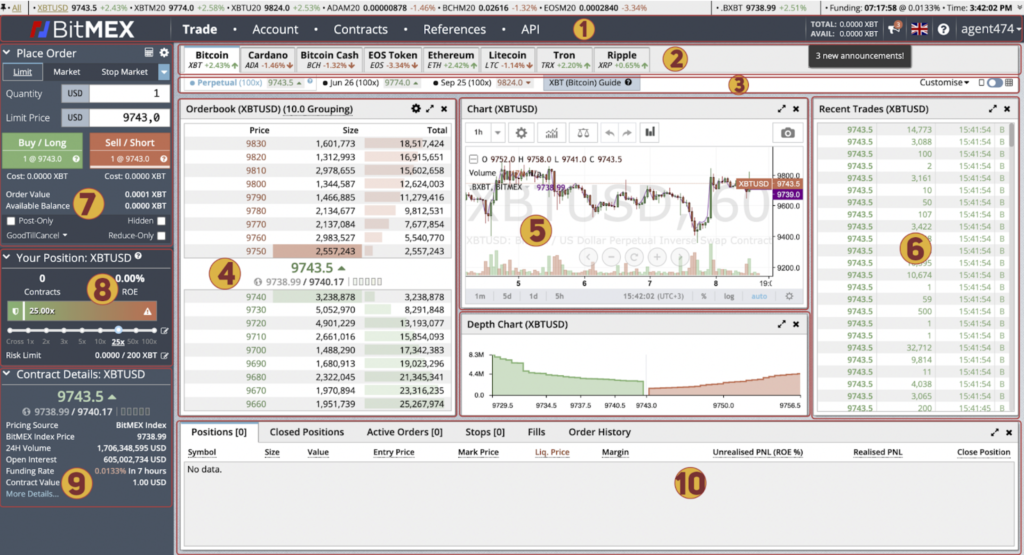
- 1. At the very top there is a bar with several tabs:
- 1.1. Trade – the main trading interface.
- 1.2. Account – the place where you can see all the needed information about your account: transaction history, deposits, withdrawals,
personal info. - 1.3. Contracts – documentation about Bitmex contracts (derivative products).
- 1.4. References – useful information about the BitMEX exchange.
- 1.5. API – all info about work with API keys.
- 2. This bar gathers the main tradable cryptocurrencies on Bitmex. Bitcoin, Ethereum, Cardano, Bitcoin Cash, Litecoin, Ripple,EOS and Tron. Click on the cryptocurrency you would like to trade.
- 3. Here are the contracts about the selected cryptocurrency.
- 4. This is the order book, you can see buy orders in green and sell orders in the red part. You also have additional information for each order, including price and quantity.
- 5. Here we can see the chart of the selected asset. All charts are provided by the TradingView. You can also deploy the chart to full screen and use all the tools and indicators available on TradingView.
- 6. The area where you can see the recent completed orders.
- 7. In this window you can choose options for a position: quantity of contracts you want to invest in the position, the price you want to buy contracts for and then open the desired position — LONG or SHORT.
- 8. In this tab, you can choose leverage before opening a position. Once you’ve taken your position, here you can see the number of contracts of your position and the return on equity in %.
- 9. Details about the contract you are trading.
- 10. At the very bottom of the screen is the widget of the positions that you have opened. If you have a limit order that hasn’t been executed yet, you can cancel it or execute it for the market price with a single click.
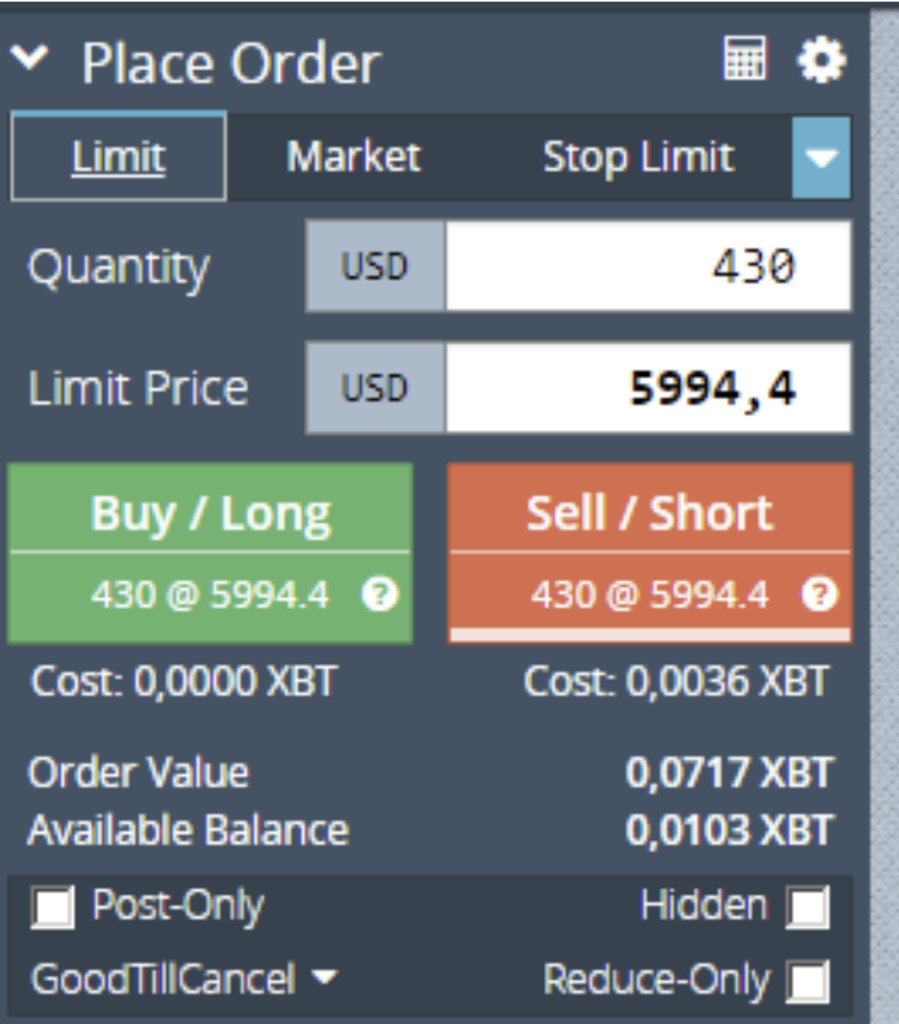
Information about opened position
After the order is executed, info about the open position appears at the bottom of the page [6 point on the screenshot of the interface].
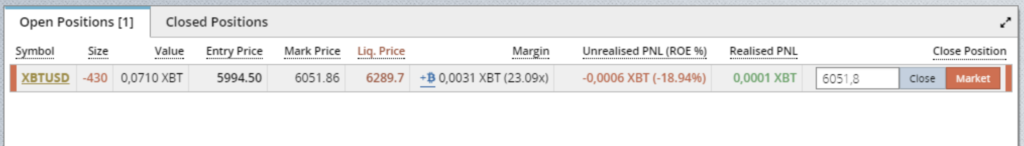
- 1. Symbol XBTUSD is the currency, bitcoin/dollar.
- 2. Size – 430 — minus means that I sold or opened a short position
- 3. Value 0.0710 XBT — position volume 0.07 btc.
- 4. Entry Price 5994.50 — I entered the position for this price.
- 5. Mark Price 6051.86 — current price, fixed at short time intervals.
- 6. Liq. Price 6289.7 — the price at which the position will be liquidated.
- 7. Margin 0.0031 (x23.09) — 0.0031 is the approximate amount of money that the exchange took from my account for opening the position.
- 8. Unrealised PNL (ROE%) – 0.0006 XBT (-18.94%) — the current result of the open position. If you close the position now, you will lose 0.0006 btc, which is -19% of the invested money.
- 9. Realized PNL 0.0001XBT — if the position is open for a long time, part of the profit is transferred to the main account and becomes available for withdrawal or opening another positions.
- 10. Close position 6051.8 — placing an order on 6051.8, which completely closes the position.
- 11. Market — the button closes the position right now with a market order. The price will not be the most profitable.
Addition. To close a position, you can place an order of the same volume, but instead of a short-long, and vice versa. You can SHORT for $500, and when the price falls heavily, put a LONG for $1000. When a $1000 order is executed, a short position of $500 will close and long for $500 open.
Order Types
Classic orders
• Limit order — this is the classical type of buy/sell orders that we set below/above the market price. For example, the market price is $8787 and you want to buy some XBT, you put the order at $8700 and as soon as price reaches this level — your order will be filled. “Quantity” means how much contracts you want to invest in the position.

• Market order — for example, you want to be 100% sure that the train won’t leave without you. In this case, you should open the market order. The meaning of it is the same as the limit order. The only difference is that you open a position for the current (!) Market price. Market orders are executed firstly, only then limit orders.
Limit Orders
I don’t recommend this type of order. If you want to take profit- you can put the limit/market order for an opposite kind of position. For example, you opened LONG at 6900$ for 100 contracts. Price reached 7100$, and you want to close your LONG position for the market price. Just open the window “market” and SELL the needed quantity of contracts.
- • Take profit market — A market order will be placed when the market reaches the Trigger Price. This type of orders can be used to set a target price on a position. It is like Stop loss, but triggers are set in an opposite direction.
- • Take profit limit — A limit order will be placed when the market reaches the Trigger Price.

Stop orders
• Stop Market (Stop loss) — is an order that automatically closes your open position in a small loss as soon as the price reaches trigger price. This type of orders works in the same way as on the others exchanges.
• Stop limit — This type of order can perform two tasks. The first task is to put a Limit Order for LONG for a price higher than the current one. For example, you want to buy BTC when it breaks through a significant resistance level which is above the current price. Then you put a limit stop order. In other words, the difference between the Limit Stop Order and the Limit Order is that you can buy an asset at a price higher than the current one. The second task is to put a Limit Stop Order for a price lower than the current one. This type of order is used for sale at a price below the current one. Usually, such type of orders is placed in the case that you expect a breakdown of an important support level.
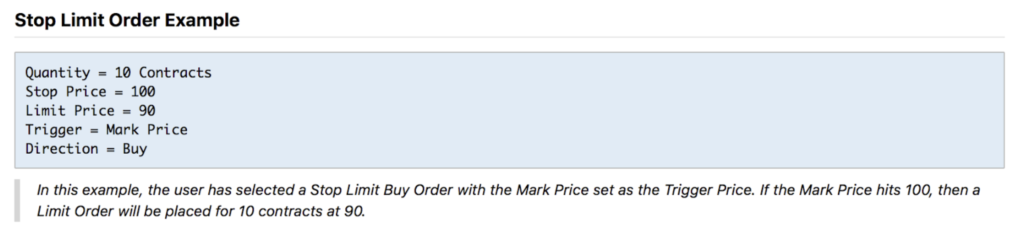
• Trailing stop — This type of stop is very similar to Market Stop, but has one advantage. For example, you think that the price will go smoothly to $9500 and don’t want to lose this profit along the way. Current market price is 8700$. You open the position with a market order (buy) or limit order just below the market price.
After the execution you set a Trail Stop Loss: set the number of contracts and trail value(example $150). After setting this stop, the order will go up with the market price, but on a distance equal to your trail value. So, for example, if the price went to the mark of 8900$ — the trail stop loss would be located at the 8750$. If the price reaches $9200 and goes down, the order will stop at the specified price (9050$) and in the case of a touch it — will close your position. If the price sharply goes up, then the order will follow it too and will be closed by the same principle, when the market “returns” back.
I advise you to put a trailing stop only in a case that you already have an opened position, not just a limit order. Another key moment: If you have opened LONG position, then put a “-” sign in the column of trail value. In a case of SHORT position- “-” isn’t needed.
Additional Information
It is crucial to check “Close on Trigger” option if you use Stop Orders. What does this thing do? This is the initiation of an order only if you already have an opened position. Otherwise, if you don’t have an opened position, but on some of the limit orders there is a “Close trigger”, then when the price reaches the Market Stop price, your limit order won’t be executed.

Useful information about the exchange
- 1. For security reasons, BitMEX exchange processes withdrawals with the manual review once a day at 13:00 UTC.
- 2. In the upper right corner of the “Place Order” window, you can find a small icon of a calculator. There you can count your profit/loss and liquidating price using different data.
- 3. Based on our personal experience, BitMEX exchange likes lagging while huge price movements are happening on the market. Thereby Bitmex can avoid sudden losses. However, traders suffer because of this.
- 4. You don’t need to send your personal data (photo of the passport) to the exchange’s support. You can deposit, withdraw and trade without any limits right after the essential registration.
- 5. The minimum deposit amount is 0.001 BTC.
- 6. If you were a newbie — we advice you to practice using orders on the test network.
